Tetracycline does indeed stain the teeth permanently, especially children under the age of 8. This is because they are still in the growing phase and teeth will are still active.
The effect of tetracycline staining teeth was first noticed in 1956 but now that professionals know this information they stop administrating this drug to pregnant women in the late stages of pregnancy and children under the age of 8.
It’s not just Tetracycline that causes tooth stains but some of its derivatives such as doxycyline and minocycline that can also affect the teeth. It’s interesting to point out that minocycline was created to combat the issue of teeth staining but unfortunately it has not really worked.
Learning about why this drug is used and what for might help everyone to come up with alternative medicine which does not cause this ugly side effect. Keep reading on and you will find out everything you need to know including some treatment options if your one of the unlucky ones.
What Is Tetracycline Used For In The First Place
Tetracycline’s were first discovered in 1945 and are a broad spectrum antibiotic found in the Streptomyces bacteria and used for treating many different bacterial infections. It is most often used to treat conditions such as:
- Severe acne
- Sexually transmitted disease
- Malaria
But can also be used if penicillin or other antibiotics fail against some of the more serious infections like Anthrax or Clostridium.
It is also on the World Health Organisations list of essential medicine needed in health care so you can see why it is used on a regular basis. It treats a lot of problems that other medicine simply can’t.
What Does Tetracycline Do To Your Teeth?
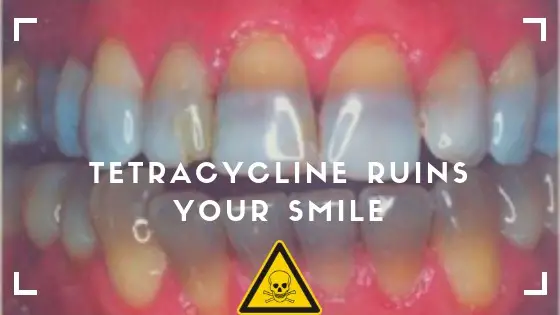
If tetracycline is given to someone who is in the process of going through mineralization and calcification, it will bind onto the calcium ions in the teeth. If this happens before a tooth has emerged from the gums, then the tetracycline bound to calcium orthophosphate will cause a yellow discoloration.
After the teeth has erupted and has been exposed to the light, tetracycline will start to oxidise causing the colour to change again from yellow to a brown colour over a period of months or years.
Permanent teeth are more likely to show a less intense but more diffuse discoloration than primary teeth.
Why Is It Not Used For Children Under 8 or Pregnant women
The reason is because this period is where calcification is at it’s most active. Deciduous teeth are affected between the age range of 10-14 months.
Anterior permanent teeth from 6 months – 6 years and the posterior permanent teeth up to the age of 8 years. Tetracycline exposure in any of these periods has the potential to cause permanent staining. This is why you see manufacturers warning us not to give children this drug.
Even though children are at the highest risk, there have been rare cases where the drug has caused staining in an adult who has been on a long term therapy plan. Statistically speaking, tetracycline induced staining is at around 3-4% and 3-6% for minocycline.
What’s Minocycline

It belongs to the same class as the tetracycline antibiotics but has a slightly wider spectrum than other drugs in this group. It has a longer half-life than other drugs which makes it active for longer.
It’s most effective against acne and other skin related problems such as MRSA.
Minocycline has three different mechanisms by which it can stain teeth unlike tetracycline.
First, the intrinsic theory, which occurs upon absorption with the minocycline molecule becoming highly protein bound and then preferentially binding to higher collagen containing tissue (i.e., teeth and bone) resulting in discoloration.
Second, the extrinsic theory is based on the high concentration of minocycline excreted in the gingival fluid and that stains by etching into the enamel where the minocycline gets oxidised (i.e., turns black) either by exposure to oxygen or bacterial activity.
Third, the binding of haemosiderin (a breakdown product of minocycline) with iron ions forms an insoluble complex within the teeth.
Given the mechanisms by which minocycline stains teeth it can stain teeth at any age, unlike tetracycline and doxycycline.
Will Teeth Be Damaged By Tetracycline?
Teeth won’t be damaged structurally or be more susceptible to cavities, the only major side effect tetracycline has is it causes severe teeth staining which in most cases can be difficult to treat. It stains deep into the surface of the tooth and has always been thought of as irreversible.
The colours of the stain vary from light yellows, dark yellows, browns, and purplish colours. Some teeth have translucent edges, large white spots on the teeth.
Can You Whiten Teeth Stained By Tetracycline?
It all depends on the severity of your stains. Once that is established you can then choose from several treatment options. These include:
- Bleaching (vital or non vital)
- Micro abrasion
- Composite and porcelain veneers
- Porcelain crowns
Bleaching

For vital tooth bleaching, there are 3 approaches you can take: In-office, At-home, dentist supervised night guarding bleaching and over the counter products.
The in office bleaching method uses high concentrations of tooth whitening agents, usually hydrogen peroxide at a concentration of 25-40%. The dentist will apply the whitening gel after protecting the gums and soft tissue by a rubber dam. The peroxide can be activated further by pointing a light to it for 40-60 minutes. This method of treatment will result in major whitening after just one session but the dentist will most likely advise that you have more sessions to reach the best results.
At home or night guarding involves using a lower concentration of whitening agents which is usually around 10-20% carbamide peroxide which is equivalent to 3.5-6.5% hydrogen peroxide. It is recommended that if your using a 15-20% carbamide solution, you use it for 3-4 hours per day.
This treatment is carried out by the patient themselves at home but should be constantly supervised by the dentist when coming back for recall visits. This method works by applying the bleaching gel through a custom fabricated mouth guard worn at night for a period of 1-2 weeks. This technique has been used for many decades and is probably the most widely used.
Over the counter Products have become ever popular in the last 3-5 years because of the simplicity and the relatively low price. These products will have a much lower concentration of whitening agent (3-6% hydrogen peroxide) and come in the shape of gum shields, strips, pre fabricated trays and toothpastes.
Data has shown that this sector of the whitening industry saw the greatest growth but you should be very thorough in your research when opting for this option because some of these bleaching agents may be questionable when it comes to safety, because some are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration.
For Non Vital bleaching there are various techniques used nowadays ranging from non-vital power bleaching, modified walking bleach and inside/outside bleaching. The walking bleach involves sealing a mixture of sodium perborate with water into the pulp chamber of the target tooth. Other times a mixture of 30% hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate are sealed into the pulp area of the tooth for 1 week.
In internal non vital power bleaching, hydrogen peroxide is placed in the pulp chamber and activated by heat. The temperature is maintained at 50-60 degrees for 5 minutes before cooling the tooth for another 5 minutes. The gel is then removed, the tooth dried. This method is used between each dental visit until the tooth is reviewed at the 2-3 week mark to see if further treatment is necessary
The inside/outside bleaching technique is a combination of internal bleaching of non-vital teeth with the home bleaching technique.
Micro Abrasion
This is a procedure whereby the enamel is removed to improve the discoloration which can be seen on the outer layer of enamel. The technique causes a loss of between 25-200μm of enamel. It’s basically carried out by mixing 18% hydrochloric acid with pumice or 10% hydrochloric acid with silica carbide particles.
Composite and porcelain veneers
Dental veneers are thin shells of porcelain or composite resin that are custom-made to fit over teeth, providing a natural, attractive look. They can be used to fix chipped, stained, misaligned, worn down, uneven or abnormally spaced teeth.
Porcelain Crowns
Crowns can replace the exterior portion of a tooth to help make it look normal again. This treatment option is best for when tooth decay has destroyed the original tooth or in cases of severe enamel erosion or discoloration.
Talk To Your Dentist on The Best Treatment

Your dentist will know better than anyone else on how severe your discoloration is and what treatment option will work best for you. It might also depend on your budget as the higher end procedures might be too expensive in which case we suggest you try out one of the over the counter whitening solutions.
We have reviewed a Teeth whitening system recently and it could be something that helps you. If your interested please take a look: Billionaire Teeth Whitening Kit Review
Conclusion
Does tetracycline stain teeth? Yes it does cause permanent tooth stains in children under 8 years old or when their in the last stages of their mothers Pregnancy. This is why it is important you avoid this antibiotic if you are in these age ranges. The drug reacts with the calcium ions and disrupts the mineralization process.
But in recent years there have been advancements in dental technologies and whitening systems that it is possible to make your teeth look much better. There are several treatment options you can choose from but make sure you consult with your dentist to find out the best solution for yourself.
If you have any questions please leave a comment below and let us help you 🙂
